By: Samantha Godden
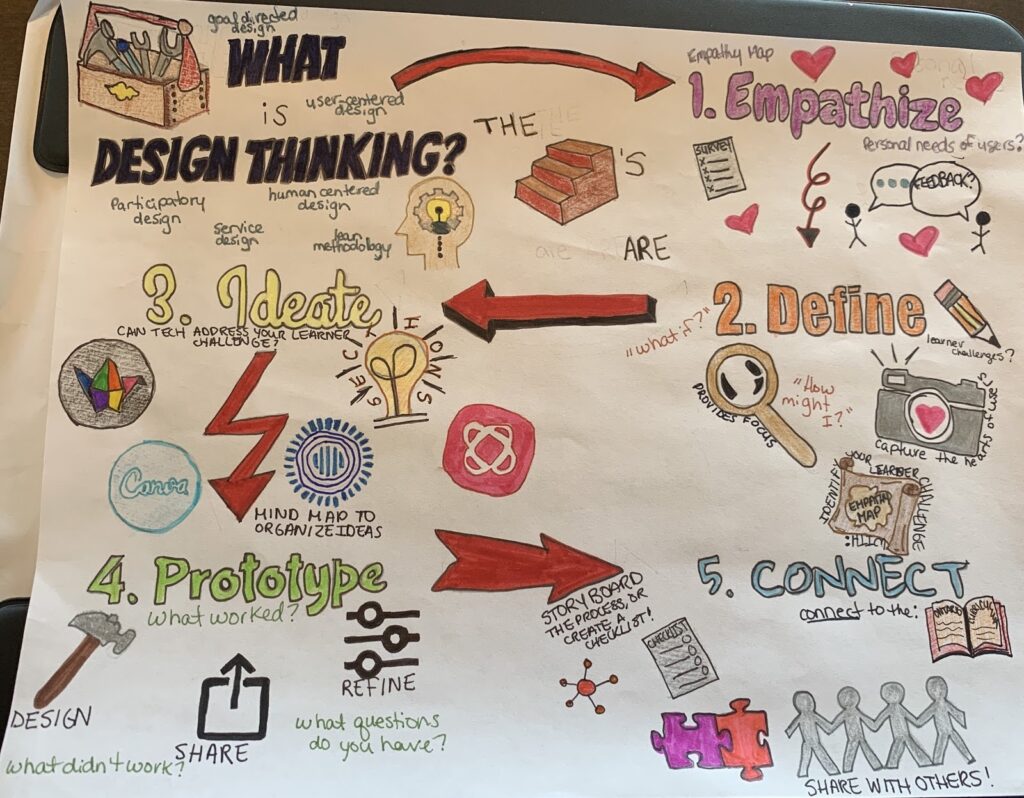
The technologist module focuses on the idea that technology tools can be used to address specific learning challenges, and that digital literacies can be used to engage and enhance student experiences. The design thinking approach is the starting point for a technologist point of view, as is a human-centered thinking approach that allows the educator to think of how the technology can benefit the student and situation. There are various methodologies and approaches to design-thinking, as it can be used in many other contexts rather than just the classroom. The module begins by explaining the approach of empathize, define, ideate, prototype and connect.
Design thinking always begins with empathy. It is important for the teacher to put themselves in the mindframe of the student. When creating activities, especially when they concern technologies, it is important to consider how everything will work towards benefitting the people involved. For an educator, it is important to empathize with the learners involved to identify a challenge that could be solved through the use of technology. If the educator is struggling with the identification of student problems, they can always ask for student feedback or create a survey.

The second step of design thinking is define. This step focuses on identifying and defining a problem or challenge facing learners. A useful tactic for this section is to create an empathy map. This allows the educator to ask themselves questions such as “what if?” or “how might I?”. When creating a good learner challenge, it is important to consider if the challenge provides focus, if it captures the heart of the learner, if it informs how subsequent ideas will be evaluated and if the concepts and plans meet the needs of the students. Once this section is completed and the learner challenge is defined, the educator is able to move onto the next section of the design thinking process.

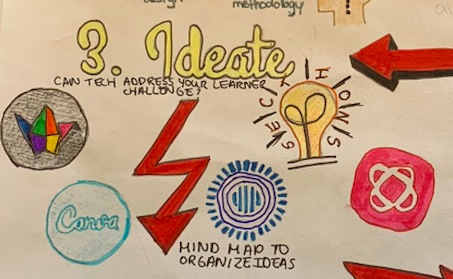
When it comes to ideate, it is important to form and build the ideal features and characteristics of how technology could address your learner challenge. Mind Mapping is a very useful tool when organizing this information and can be done on a variety of platforms. I tried to outline the various websites in my sketchnote, such as Padlet, Canva, Prezi and Mindmeister. After the mind mapping is complete, the next step is to choose a technology tool to help address your challenge. Using the SECTIONS model might be useful in this section, as it allows the educator to ensure the technology model is the right fit for the students.
After the ideate section, the user should have chosen their respective technology. They can then move to the prototype section, where they can see if their technology would be successful for their intended audience and receive feedback from users. The steps of the prototype section are: design, share and refine. The design section involves playing around with the chosen technology and seeing if it would work as successfully as previously thought. The second section is share, which involves sharing your ideas with peers and learners in order to receive feedback and see what worked and what could be improved. Finally, once feedback is received, we move to the refine section, where the educator can take the necessary steps in order to improve their ideas and designs.

Finally, the last section of this module focuses on connection. It is important to connect the lesson and technology to the ontario curriculum, as well as your intended learning outcomes. This will ensure that students can see how technology integration is important to their learning and can be useful for their futures.